Disease-causing variants in the non-coding genome
Despite extensive testing involving whole genome sequencing over 50% of patients with developmental disorders remain without a genetic diagnosis. This diagnostic gap exposes the limitations of current technologies to detect and interpret disease-causing mutations. For instance, whole genome sequencing can detect mutations throughout the genome but pinpointing a disease-causing mutation among hundreds of thousands of benign variants remains a daunting task. Thus, accurate identification of disease-causing mutations, especially in non-coding regions of the genome, currently represents a major challenge in human genetics.
So far, the non-coding genome has not been the focus of human genetics and Mendelian disease research on non-coding variants is only slowly emerging. This is mainly due to a large number of variants per genome and difficulties in interpreting non-coding variants. Together, this poses major problems that partially require the use of other/new technologies as well as new concepts of thinking and data interpretation. Our lab focuses on elucidating the patho-mechanisms underlying disease-causing mutations in the non-coding genome. Since there is currently no general concept to interpret mutations in the non-coding genome for their ability to cause disease, it is the aim of our group to develop such a framework and predict the regulatory effect of structural variations (SVs) in a disease setting.
To address this challenge, we are applying state-of-the-art functional genomics technologies to identify pathogenic mutations underlying human developmental disease and dissect the molecular mechanism through which these alterations disrupt human development. Our research aims to better understand the genetic causes and mechanisms of currently unsolved developmental disorders. Ultimately, our goal is to translate results from basic research carried out at the lab bench into the clinic by improving current methods of genetic diagnosis and setting a base on which to provide better medical treatment and accurate genetic counselling to individuals affected by developmental disorders.
Publications
1.
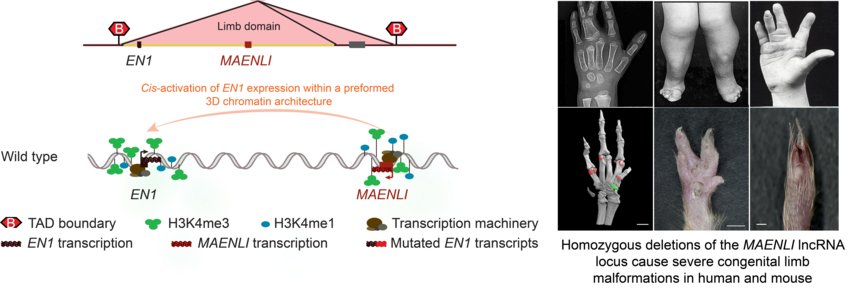
Lila Allou, Sara Balzano, Andreas Magg, Mathieu Quinodoz, Beryl Royer-Bertrand, Robert Schöpflin, Wing-Lee Chan, Carlos E. Speck-Martins, Daniel Rocha Carvalho, Luciano Farage, Charles Marques Lourenço, Regina Albuquerque, Srilakshmi Rajagopal, Sheela Nampoothiri, Belinda Campos-Xavier, Carole Chiesa, Florence Niel-Bütschi, Lars Wittler, Bernd Timmermann, Malte Spielmann, Michael I. Robson, Alessa Ringel, Verena Heinrich, Giulia Cova, Guillaume Andrey, Cesar A. Prada-Medina, Rosanna Pescini-Gobert, Sheila Unger, Luisa Bonafé, Phillip Grote Carlo Rivolta Stefan Mundlos✉ & Andrea Superti-Furga
Non-coding deletions identify Maenli lncRNA as a limb-specific En1 regulator
Nature (2021)
2.
, Marion Rivalan, Friederike S. David, Alexander Stumpf, Julika Pitsch, Despina Tsortouktzidis, Laura Moreno Velasquez, Anne Voigt, Karl Schilling, Daniele Mattei, Melissa Long, Guido Vogt, Alexej Knaus, Björn Fischer-Zirnsak, Lars Wittler, Bernd Timmermann, Peter N. Robinson, Denise Horn, Stefan Mundlos, Uwe Kornak, Albert J. Becker, Dietmar Schmitz, York Winter, and Peter M. Krawitz
A CRISPR-Cas9–engineered mouse model for GPI-anchor deficiency mirrors human phenotypes and exhibits hippocampal synaptic dysfunctions
PNAS January 12, 2021 118 (2) e2014481118
3.
Suzanne E. de Bruijn, Alessia Fiorentino, Daniele Ottaviani, Stephanie Fanucchi, Uirá S. Melo, Julio C. Corral-Serrano, Timo Mulders, Michalis Georgiou, Carlo Rivolta, Nikolas Pontikos, Gavin Arno, Lisa Roberts, Jacquie Greenberg, Silvia Albert, Christian Gilissen, Marco Aben, George Rebello, Simon Mead, F. Lucy Raymond, Jordi Corominas, Claire E.L. Smith, Hannie Kremer, Susan Downes, Graeme C. Black, Andrew R. Webster, Chris F. Inglehearn, L. Ingeborgh van den Born, Robert K. Koenekoop, Michel Michaelides, Raj S. Ramesar, Carel B. Hoyng, Stefan Mundlos, Musa M. Mhlanga, Frans P.M. Cremers, Michael E. Cheetham, Susanne Roosing,* and Alison J. Hardcastle*
Structural Variants Create New Topological-Associated Domains and Ectopic Retinal Enhancer-Gene Contact in Dominant Retinitis Pigmentosa
Am J Hum Genet. 2020 Nov 5;107(5):802-814.
4.
Uira Souto Melo*, Robert Schöpflin*, Rocio Acuna-Hidalgo*, Martin Atta Mensah, Björn Fischer-Zirnsak, Manuel Holtgrewe, Marius-Konstantin Klever, Seval Tu¨rkmen, Verena Heinrich, Ilina Datkhaeva Pluym, Eunice Matoso, Sergio Bernardo de Sousa, Pedro Louro, Wiebke Hülsemann, Monika Cohen, Andreas Dufke, Anna Latos-Biele�nska, Martin Vingron, Vera Kalscheuer, Fabiola Quintero-Rivera, Malte Spielmann,* and Stefan Mundlos*
Hi-C Identifies Complex Genomic Rearrangements and TAD-Shuffling in Developmental Diseases
The American Journal of Human Genetics (2020), Volume 106, Issue 6, 872 - 884
5.
Spielmann M, Lupiáñez DG, Mundlos S.
Structural variation in the 3D genome.
Nat Rev Genet. 2018 Jul;19(7):453-467. Review.
6.
Flöttmann R, Kragesteen BK, Geuer S, Socha M, Allou L, Sowińska-Seidler A, Bosquillon de Jarcy L, Wagner J, Jamsheer A, Oehl-Jaschkowitz B, Wittler L, de Silva D, Kurth I, Maya I, Santos-Simarro F, Hülsemann W, Klopocki E, Mountford R, Fryer A, Borck G, Horn D, Lapunzina P, Wilson M, Mascrez B, Duboule D, Mundlos S, Spielmann M.
Noncoding copy-number variations are associated with congenital limb malformation.
Genet Med. 2018 Jun;20(6):599-607. Epub 2017 Oct 12
7.
Knaus A, Pantel JT, Pendziwiat M, Hajjir N, Zhao M, Hsieh TC, Schubach M, Gurovich Y, Fleischer N, Jäger M, Köhler S, Muhle H, Korff C, Møller RS, Bayat A, Calvas P, Chassaing N, Warren H, Skinner S, Louie R, Evers C, Bohn M, Christen HJ, van den Born M, Obersztyn E, Charzewska A, Endziniene M, Kortüm F, Brown N, Robinson PN, Schelhaas HJ, Weber Y, Helbig I, Mundlos S, Horn D, Krawitz PM.
Characterization of glycosylphosphatidylinositol biosynthesis defects by clinical features, flow cytometry, and automated image analysis.
Genome Med. 2018 Jan 9;10(1):3
8.
Spielmann M, Hernandez-Miranda LR, Ceccherini I, Weese-Mayer DE, Kragesteen BK, Harabula I, Krawitz P, Birchmeier C, Leonard N, Mundlos S.
Mutations in MYO1H cause a recessive form of central hypoventilation with autonomic dysfunction.
J Med Genet. 2017 Nov;54(11):754-761. Epub 2017 Aug 4.
9.
Afzal M, Zaman Q, Kornak U, Mundlos S, Malik S, Flöttmann R.
Novel splice mutation in LRP4 causes severe type of Cenani-Lenz syndactyly syndrome with oro-facial and skeletal symptoms.
Eur J Med Genet. 2017 Aug;60(8):421-425. Epub 2017 May 27.
10.
Spielmann M, Kakar N, Tayebi N, Leettola C, Nürnberg G, Sowada N, Lupiáñez DG, Harabula I, Flöttmann R, Horn D, Chan WL, Wittler L, Yilmaz R, Altmüller J, Thiele H, van Bokhoven H, Schwartz CE, Nürnberg P, Bowie JU, Ahmad J, Kubisch C, Mundlos S, Borck G.
Exome sequencing and CRISPR/Cas genome editing identify mutations of ZAK as a cause of limb defects in humans and mice.
Genome Res. 2016 Feb;26(2):183-91.
11.
Flöttmann R, Wagner J, Kobus K, Curry CJ, Savarirayan R, Nishimura G, Yasui N, Spranger J, Van Esch H, Lyons MJ, DuPont BR, Dwivedi A, Klopocki E, Horn D, Mundlos S, Spielmann M.
Microdeletions on 6p22.3 are associated with mesomelic dysplasia Savarirayan type.
J Med Genet. 2015 Jul;52(7):476-83. Epub 2015 Jun 1.
12.
Lelieveld SH, Spielmann M, Mundlos S, Veltman JA, Gilissen C.
Comparison of Exome and Genome Sequencing Technologies for the Complete Capture of Protein Coding Regions.
Hum Mutat. 2015 Aug;36(8):815-22. Epub 2015 Jun 11.
13.
Ehmke N, Caliebe A, Koenig R, Kant SG, Stark Z, Cormier-Daire V, Wieczorek D, Gillessen-Kaesbach G, Hoff K, Kawalia A, Thiele H, Altmüller J, Fischer-Zirnsak B, Knaus A, Zhu N, Heinrich V, Huber C, Harabula I, Spielmann M, Horn D, Kornak U, Hecht J, Krawitz PM, Nürnberg P, Siebert R, Manzke H, Mundlos S.
Homozygous and compound-heterozygous mutations in TGDS cause Catel-Manzke syndrome.
Am J Hum Genet. 2014 Dec 4;95(6):763-70.
14.
Lohan S, Spielmann M, Doelken SC, Flöttmann R, Muhammad F, Baig SM, Wajid M, Hülsemann W, Habenicht R, Kjaer KW, Patil SJ, Girisha KM, Abarca-Barriga HH, Mundlos S, Klopocki E.
Microduplications encompassing the Sonic hedgehog limb enhancer ZRS are associated with Haas-type polysyndactyly and Laurin-Sandrow syndrome.
Clin Genet. 2014 Oct;86(4):318-25. Epub 2014 Feb 17.
15.
Zemojtel T, Köhler S, Mackenroth L, Jäger M, Hecht J, Krawitz P, Graul-Neumann L, Doelken S, Ehmke N, Spielmann M, Oien NC, Schweiger MR, Krüger U, Frommer G, Fischer B, Kornak U, Flöttmann R, Ardeshirdavani A, Moreau Y, Lewis SE, Haendel M, Smedley D, Horn D, Mundlos S, Robinson PN.
Effective diagnosis of genetic disease by computational phenotype analysis of the disease-associated genome.
Sci Transl Med. 2014 Sep 3;6(252):252ra123.
16.
Tayebi N, Jamsheer A, Flöttmann R, Sowinska-Seidler A, Doelken SC, Oehl-Jaschkowitz B, Hülsemann W, Habenicht R, Klopocki E, Mundlos S, Spielmann M.
Deletions of exons with regulatory activity at the DYNC1I1 locus are associated with split-hand/split-foot malformation: array CGH screening of 134 unrelated families.
Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2014 Jul 29;9:108.
17.
Girisha KM, Bidchol AM, Kamath PS, Shah KH, Mortier GR, Mundlos S, Shah H.
A novel mutation (g.106737G>T) in zone of polarizing activity regulatory sequence (ZRS) causes variable limb phenotypes in Werner mesomelia.
Am J Med Genet A. 2014 Apr;164A(4):898-906. Epub 2014 Jan 29.